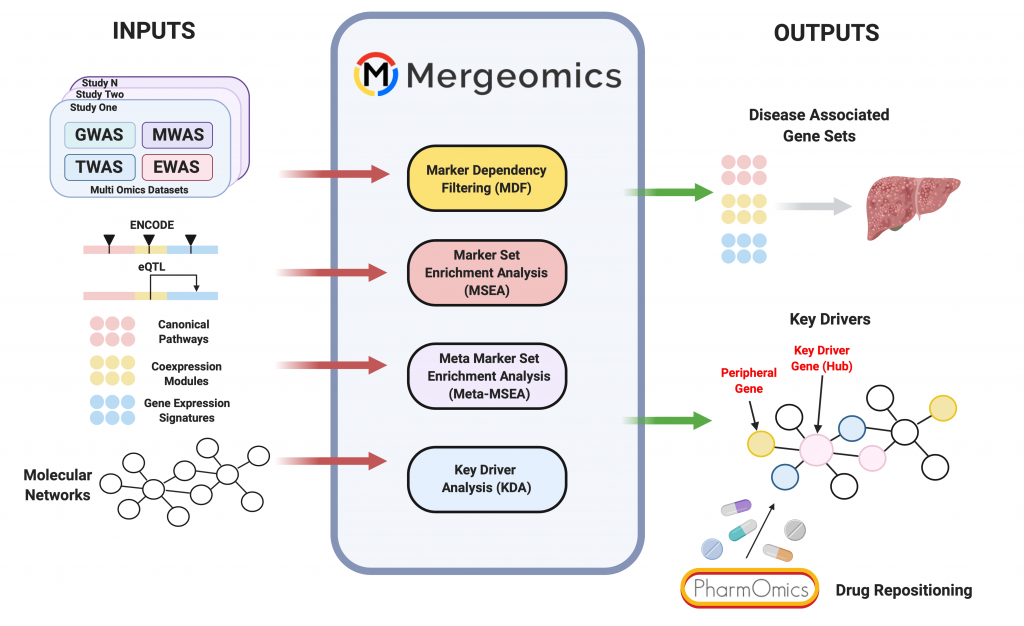
The Mergeomicsweb server allows for multi-omics data integration to derive biological pathways, networks, and key drivers important to disease pathogenesis. Multi-omics data types that can be integrated include full summary statistics of disease associations, such as from genome-, epigenome-, and transcriptome-wide association studies, and functional genomics data such as expression quantitative trait loci and gene network models.
Currently, only a few multi-omics integration tools are available, and Mergeomics uniquely accommodates diverse data types from different sources, studies, or species for a given disease. Mergeomics uses summary statistics, not raw data, thereby removing the need for additional data processing and widening its application potential. Mergeomics has the ability to model gene regulatory networks and predict and visualize network regulators of disease. These unique features help maximize the utility of existing datasets and overcome the limitations of other tools.
Mergeomics has been applied to numerous complex diseases including coronary artery disease, diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and psoriasis. In each case, in vivo, in vitro, and/or in silico cross-validation strongly support novel biological predictions. Since the first version of our Mergeomics web server, we have made major efforts to redesign the user interface, simplify workflows, offer detailed tutorials and case studies, and provide more datasets and network models for utilization. The Mergeomics 2.0 webserver offers the scientific community much-improved accessibility to our pipeline, caters to each user’s specific goals in multi-omics studies, and addresses a broad range of biological questions.
Mergeomics webpage : http://mergeomics.research.idre.ucla.edu/
Developed by Yang lab in integrative biology and physiology department



